01 Diamond
First of all, let's understand what the protagonist of diamond polishing agent-diamond is.
The diamond powder used in the diamond polishing agent is mostly artificial diamond, which is composed of C atoms, and the C atoms are all bonded by covalent bonds. The basic law of atomic arrangement is that each C atom is surrounded by 4 C atoms distributed in regular tetrahedrons. These C atoms are neatly arranged in a tetrahedral structure, and each C atom is directly and closely connected with other 4 C atoms to form a solid crystal, so it is particularly hard (the hardest substance in nature). The hardness of diamond can reach Mohs hardness level 10, the microhardness is 150 times higher than that of corundum (Al2O3), and it has extremely high wear resistance, which is 90 times higher than that of corundum. Therefore, diamond polishing agent can be used to polish very hard materials such as cemented carbide, ceramics, etc., which cannot be achieved by polishing agents such as alumina.
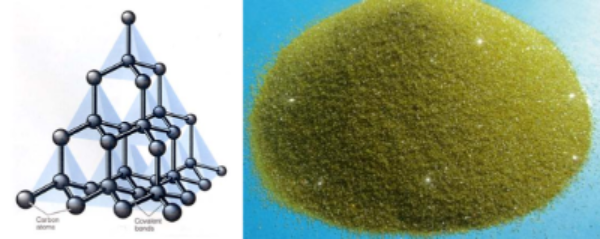
At the same time, diamond crystals are rich in crystal forms, such as octahedron, rhombic dodecahedron, cube, tetrahedron and hexagonal octahedron. These sharp edges and corners make the diamond have a strong cutting ability, which can improve the polishing efficiency, and has a good cutting effect on soft and hard materials. If there are phases with great differences between hard and soft phases in the alloy, good results can be obtained by polishing with diamond micropowder.
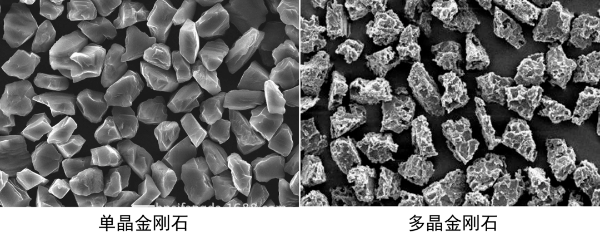
The morphology of diamond can be divided into single crystal and polycrystalline. Single crystal diamond is a crystal combined with saturated and directional covalent bonds, so it has extremely high hardness and wear resistance. Polycrystalline diamond (micropowder) is made from graphite using a unique directional blasting method. The shock wave of the directional blasting of high-explosive explosives accelerates the flight of metal flyers and hits the graphite sheet, resulting in the conversion of graphite into polycrystalline diamond. Its structure is very similar to that of natural diamond, and it is formed by unsaturated bonds and has good toughness. The structure of polycrystalline diamond is very similar to that of natural black diamond, which is composed of spherical crystallites, and the crystallite size is only 3-10nm. Therefore, it is self-sharpening compared to single crystal diamond. Polycrystalline diamond has a higher removal rate and toughness, and is less prone to scratching the surface. It is more suitable for grinding workpieces whose surface is made of different hardness materials.
In addition, during the polishing process, the diamond polishing agent basically produces grinding action, with little rolling action, so the surface deformation layer and Bayer layer (amorphous layer produced by surface metal flow) hardly produce or affect the layer even Thin.
01 Diamond polish
Diamond polishing agents are mostly supplied as diamond polishing suspensions, diamond polishing pastes and diamond sprays. Its commonly used particle sizes are 15μm, 9μm, 6μm, 3μm and 1μm. When used, it can follow the 1/3 rule that the size of the next polishing particle is the upper polishing particle. Among them, 15μm (equivalent to P1200 sandpaper) is generally used to replace the grinding of finer sandpaper. General metal materials can be directly polished with 3μm diamond after being ground with P1200 sandpaper.
Diamond polishing compound is often used in conjunction with hard woven or short-pile polishing cloths.
1)Diamond Polishing Suspension
Diamond polishing suspensions are mostly supplied in the metallographic industry in the form of single crystals and polycrystals. It is composed of high-quality diamond micropowder, composite dispersant and dispersion medium, with various formulations, which can cope with different polishing processes and workpieces, and has strong applicability. The product has good dispersion, uniform particle size and stable quality, and is widely used in grinding and polishing of hard materials.
Single crystal diamond polishing liquid has good cutting force, and its cost is relatively low. It is widely used in the polishing of superhard materials, such as most hard non-ferrous metals, ferrous metals, hard alloys, ceramics and minerals. Polycrystalline diamond polishing fluid utilizes the characteristics of polycrystalline diamond. It maintains high cutting efficiency during the grinding and polishing process and is not easy to scratch the workpiece. When it is necessary to efficiently prepare more perfect and finer metallographic samples, polycrystalline diamond polishing fluid is a rare choice. In addition to the applicable materials for single crystal diamond polishing fluid, it can also be used for grinding and polishing of sapphire substrates, optical crystals, hard glass and crystals, superhard ceramics and alloys, magnetic heads, hard disks, chips and other fields.
When in use, evenly spray an appropriate amount of diamond polishing liquid on the polishing cloth through the spray head or a pickaxe bottle, and do not use too much. Some people blindly believe that the more polishing fluid sprayed, the faster the polishing. This is a long-standing misunderstanding. In fact, because too much polishing liquid isolates the polishing surface of the sample and the polishing cloth, it will lead to a decrease in polishing efficiency. At the same time, it will also waste polishing liquid and increase production costs. Never mix different grit sizes on the same polishing cloth, this will create scratches that are difficult to remove. For some samples that need to check the real porosity, it needs to be polished with 3μm polishing solution for a long time.
In addition, when the polished material is prone to chemical reactions with water, oil-based or anhydrous diamond polishing fluid should be used for polishing.

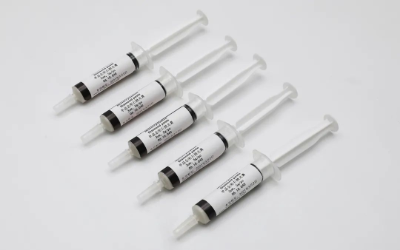
2)Diamond polishing paste
Diamond abrasive paste is a kind of soft polishing agent made of diamond micropowder abrasive and paste binder. The paste is divided into water-soluble and oil-soluble, with good lubricating and cooling properties. Oil-soluble abrasive paste has good wettability, small grinding force and heat, and is mainly used for polishing the metallography of high-hard materials, such as instruments, measuring tools, cutting tools, abrasive tools, etc. Water-soluble abrasive paste has low viscosity, easy cutting, and high processing efficiency. It is mainly used for polishing, circuit boards, glass, ceramics, gemstones, agate and other non-metallic hard and brittle materials. When using the polishing paste, draw an "X" shape with the center of the polishing cloth as the intersection point. Since the paste has a lubricating effect, polishing paste can be considered for some softer materials that are prone to scratches.
3)Diamond spray
Diamond spray is a suspension of abrasive micropowder added with wetting agent and distilled water. It is installed in a sealed metal tank. There is a certain pressure in the tank. Press the top button, and the suspension will be evenly sprayed on the sprayed fabric in the form of mist. It is characterized by convenient and quick use and even spraying. The amount of spray liquid can be reasonably controlled and the cost can be saved. However, it should be pointed out that some diamond sprays contain more organic solvents, which may cause dirt on the polishing surface. For this reason, water polishing should be carried out in the last 15~30s near the end of polishing to obtain a bright and stain-free surface.

Common application parameters of diamond polishing fluid
|
Applied Materials |
Particle Size of diamond Polishing Fluid /μm |
Single Specimen Load /N |
speed of bottom plate /rpm |
TIME:/min:sec |
|
hardened steel |
3 |
25 |
120~150 same direction |
02:00 |
|
aluminum |
1 |
20 |
120~150 same direction |
02:00~05:00 |
|
copper |
1 |
20 |
120~150 same direction |
03:00~05:00 |
|
stainless steel |
3 |
20 |
120~150 same direction |
02:00 |
|
PCB |
1 |
20 |
120~150 same direction |
02:00 |
|
ceramics |
3 |
25 |
120~150 same direction |
02:00~05:00 |
|
thermal spray coating |
3 |
20 |
120~150 same direction |
05:00~15:00 |
|
carbonfiber composite |
3 |
20 |
120~150 same direction |
02:00~05:00 |
|
general steels |
1 |
25 |
120~150 same direction |
02:00~05:00 |
|
* Some aluminum will react with water to cause the polished surface to turn black, and oil-based or water-free polishing fluid can be used. In addition, adding oil-based lubricants when using ordinary polishing fluid can also effectively prevent the polishing surface from turning black; * When fine processing is required, diamond polishing agent can only be used as coarse and medium polishing; * The above data is applicable to the sample of φ30mm. |
||||
Diamond polishing compound is generally used as a rough and medium polishing, even for very hard materials, it can be refined with other polishing liquids (such as silicon dioxide) to obtain a perfect scratch-free surface.

 中文简体
中文简体 英语
英语 西班牙语
西班牙语 德语
德语


.png?imageView2/2/w/400/format/jpg/q/75)

.jpg?imageView2/2/w/400/format/jpg/q/75)












